Back to top
Whole Exome Sequencing

Use whole exome sequencing to:
- Focus on selected regions and small variations within a genome
- Confine observations to the protein coding regions of a genome in a diagnostic related setting
- Reduce costs and turnover time for recurrent detection in a long term study
Overview
Considerations before starting a whole exome sequencing project:
- Which organism and reference genome?
- Aim of the study?
- Required coverage?
Let us guide you – from design to analysis
Example projects using whole exome sequencing:
- Single nucleotide variations (SNVs) and small insertions and deletions (InDels) observations for cancer samples
- Comparing SNV profiles
- Time series observation of mutagen treatment consequences on protein modification
Applications related to whole exome sequencing:
- Eukaryotic resequencing
- Microsatellite marker development
Workflow
A typical workflow for a whole exome sequencing project is shown in the graphic below. Please note that our highly-modular processes allow you various entry and opting out options. If you outsource your entire NGS project to Microsynth or only parts of it is up to you.
Results
The results produced by our analysis module help answer two main questions of a resequencing of a eukaryotic exome aiming at detecting variations to a pre-annotated reference exome.
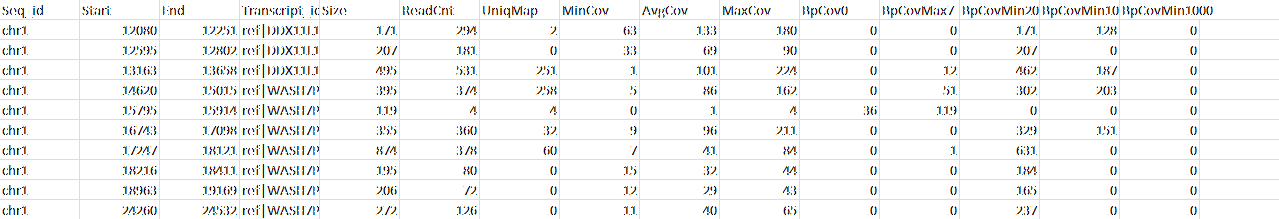
- How well was the target exome covered? (see Table 1)
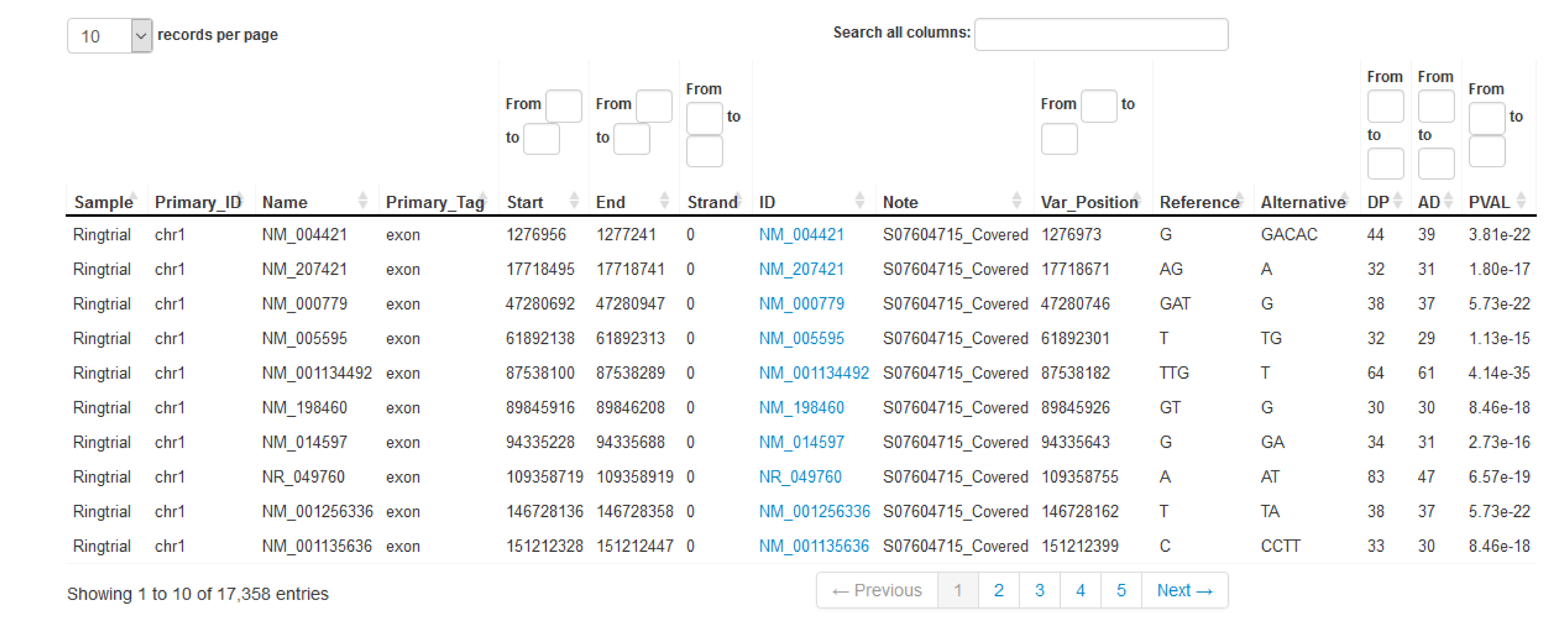
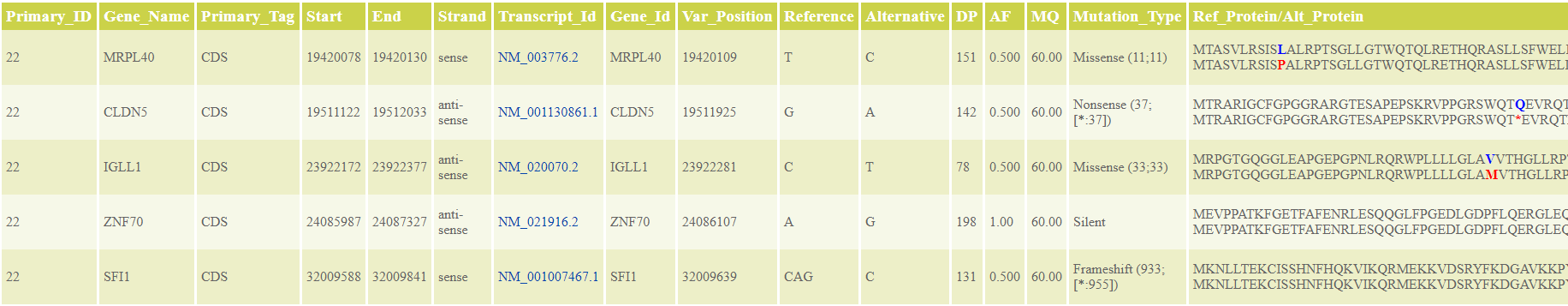
- Which are the single nucleotide variations and small insertions/deletions in comparison to the reference genome and which are the effects of these detected variations on the protein level? (see Tables 2A and 2B)
- Which of the detected variations are also known and listed in public databases (e.g., ClinVar - NCBI - NIH)? (see Table 3)
Table 1: This is a cutout of the full table detailing read coverage for every target in the sequenced exome.
Turnaround Time
- Delivery of data within x working days upon sample receipt (includes library preparation and sequencing)
- Additional x working days for data analysis (bioinformatics)
- Express service possible on request
x= on request